Magnetic Interactions in Covalently Linked [Mn3]-dimer Single-Molecule Magnets
Jie-Xiang Yu, Dian-Teng Chen, and Hai-Ping Cheng
Department of Physics, Center for Molecular Magnetic Quantum Materials, and Quantum Theory Project, University of Florida, Gainesville, FL 32603
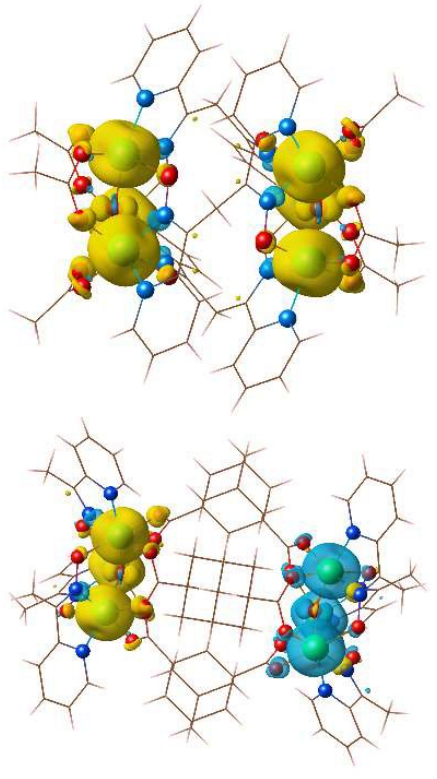
A large family of Mn-based single-molecule magnets (SMM) have been synthesized and studied in their crystalline forms. Because of the extremely weak inter-molecule interaction, experimental measurements are often carried out to study single molecule properties rather than crystalline properties. In recent years, crystalline of dimers trimers and tetramers of SMM have been also made, enriching greatly spin couplings in nanomagnetic systems.
In this work, we investigate via first-principles calculations the magnetic interactions of two kinds of covalently linked dimer of [Mn3O(O2CMe)3] ([Mn3]) single-molecule magnets, ([Mn3]2-dpd)2+ and ([Mn3]2-ada)2+ (shown in Figure). Each [Mn3] molecule is in a S = 6 high spin state, where each Mn shows +3 valence state with S = 2 spin state. One ([Mn3]2-dpd)2+ dimer displays ferromagnetic (FM) coupling between molecules, while one ([Mn3]2-ada)2+ dimer is antiferromagnetic (AF). These results agree with experimental observations by our collaborators. We further study effects of external pressure on the magnetic interaction by changing the lattice constant.
Acknowledgment: This work is supported by the DOE/BES EFRC program. Structures of Mn3- dimers are provided by Professor Christou’s group.